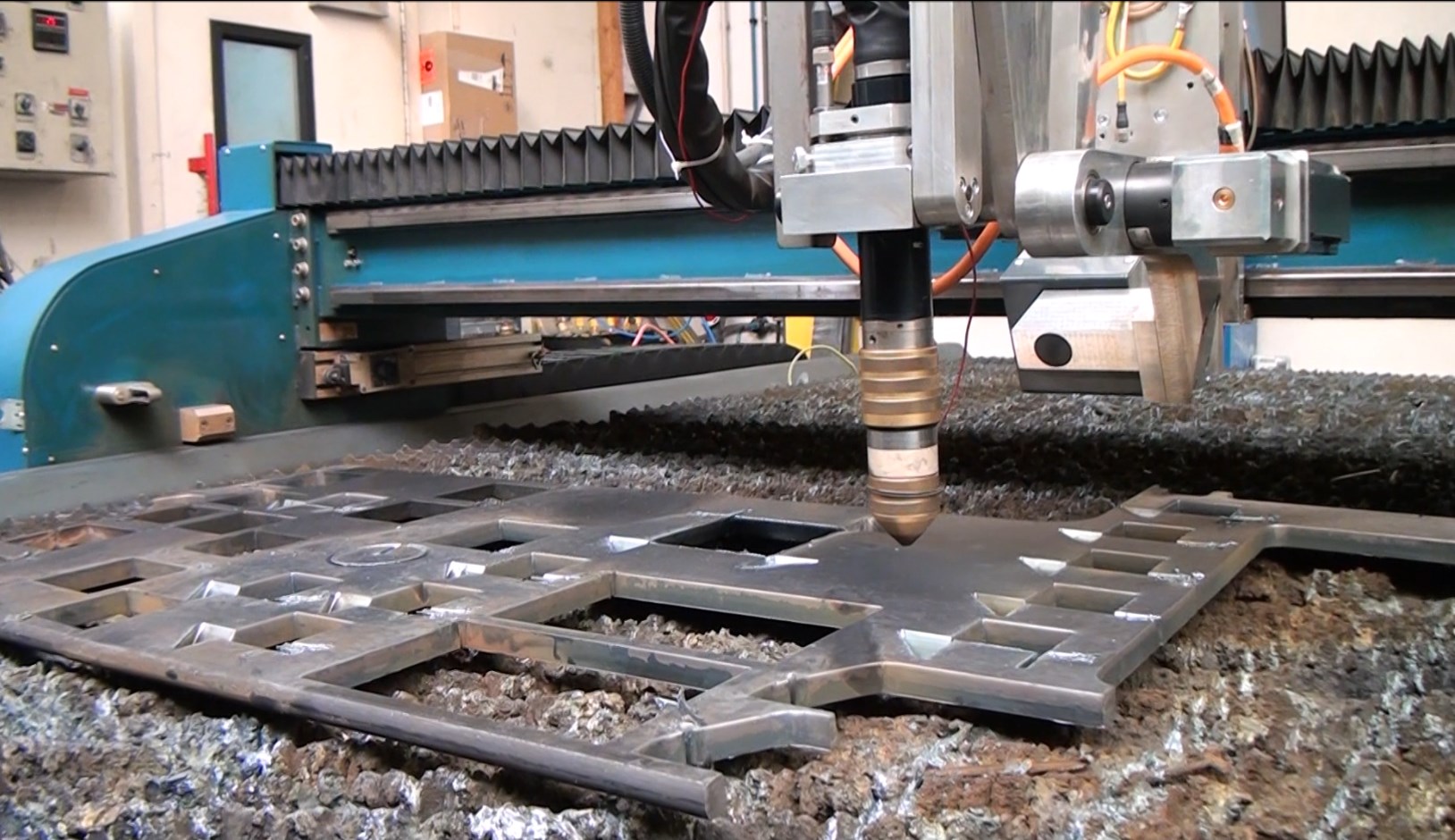
Plasma cutting of plates
Plasma cutting is a melting technique used for cutting steel, stainless steel and aluminium sheet metal plates. (all conductive plates). This technique is precise and closely approaches the quality of laser cutting.
We cut your test pieces without obligation and are happy to give you more information about our special training and service.
Contact usPlasma cutting is a melting technique used for cutting steel, stainless steel and aluminium sheet metal plates. (all conductive plates). This technique is precise and closely approaches the quality of laser cutting.
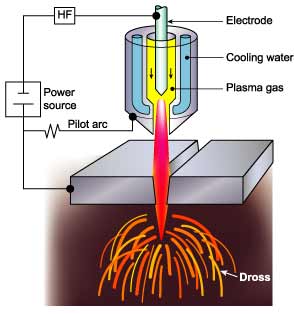
The plasma cutting proces begins with cutting gas that is moved to the nozzle of the plasma torch. there it is pushed outside through a small hole where it makes contact with electricity and becomes ionised gas, also called plasma.
The torch contains a negatively charged electron while the work piece is positively charged. This causes a small and stable electrical arc with a high energy density. The high temperature (up to 25000 C) melts the metal away that then is removed by the plasma gas.
In contrast to oxy-fuel cutting there is no burning. This allows for a precise cut with bot low as high alloy metals (steel, stainless steel, aluminium) as special steel types such as: Hardox® wear plate, Domex, Dillidur, Strenx®, Dillimax, Strenx.
The plasma cutter is capable of 2 techniques that simplify the production proces of can lead to savings in production costs. These techniques are engraving and bevel cutting.
A plasma cutter is capable of engraving. Practically this means that is possible to indicate edges, centering points for holes as well as production codes, identification numbers and drawing numbers. This may improve the construction speed and traceability.

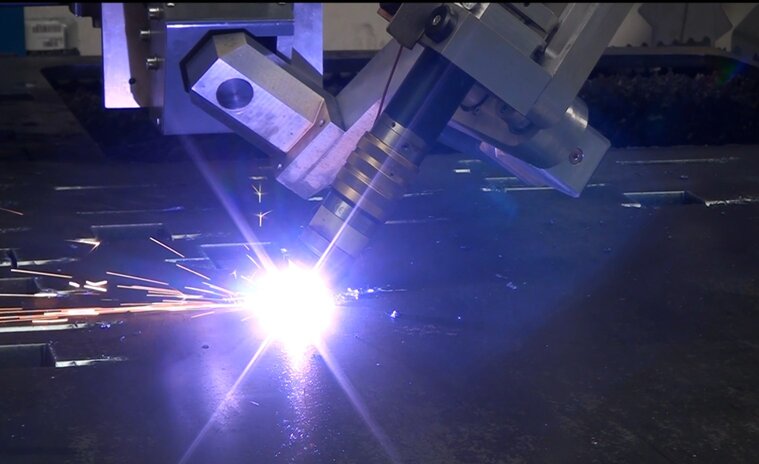
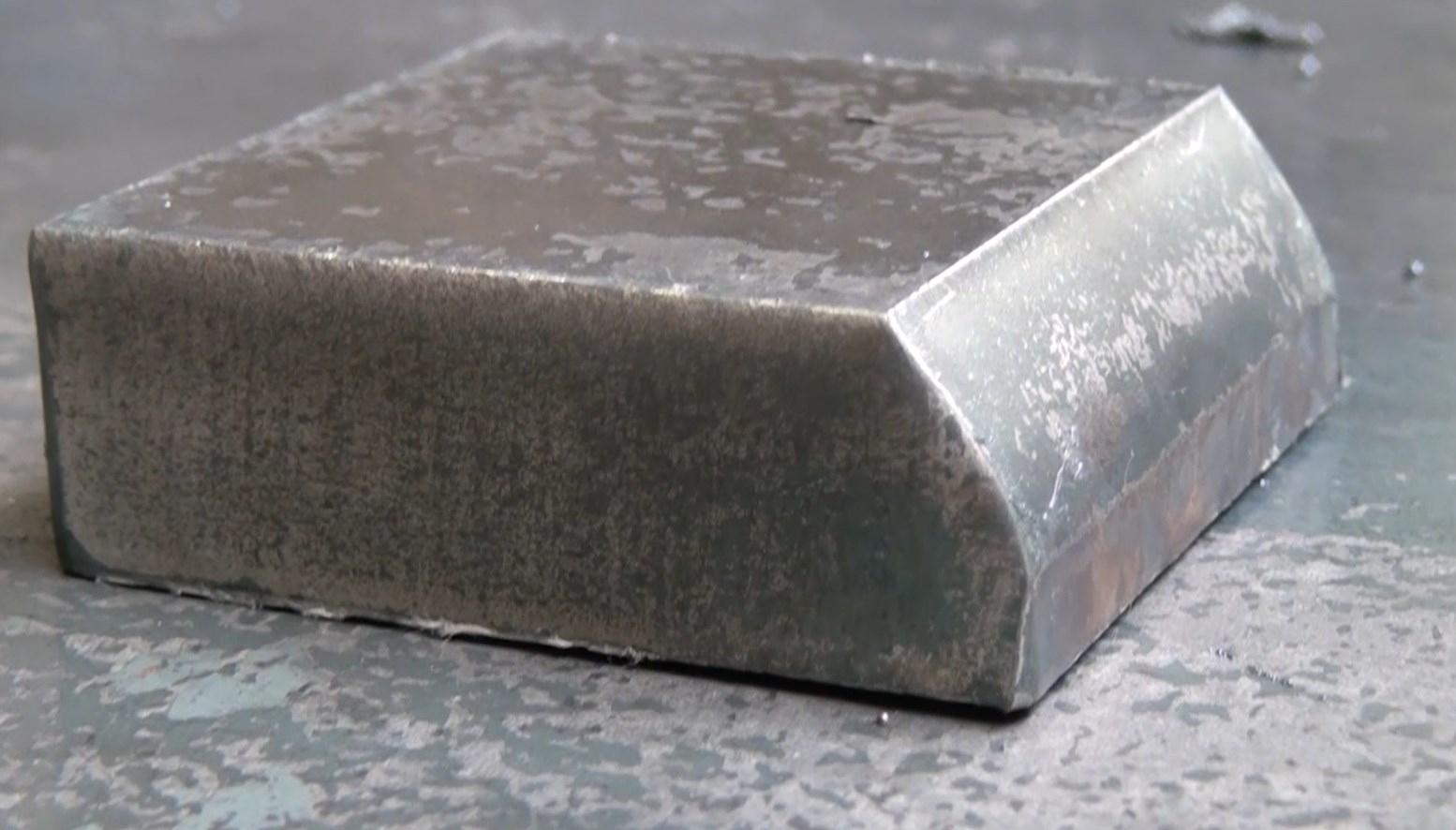
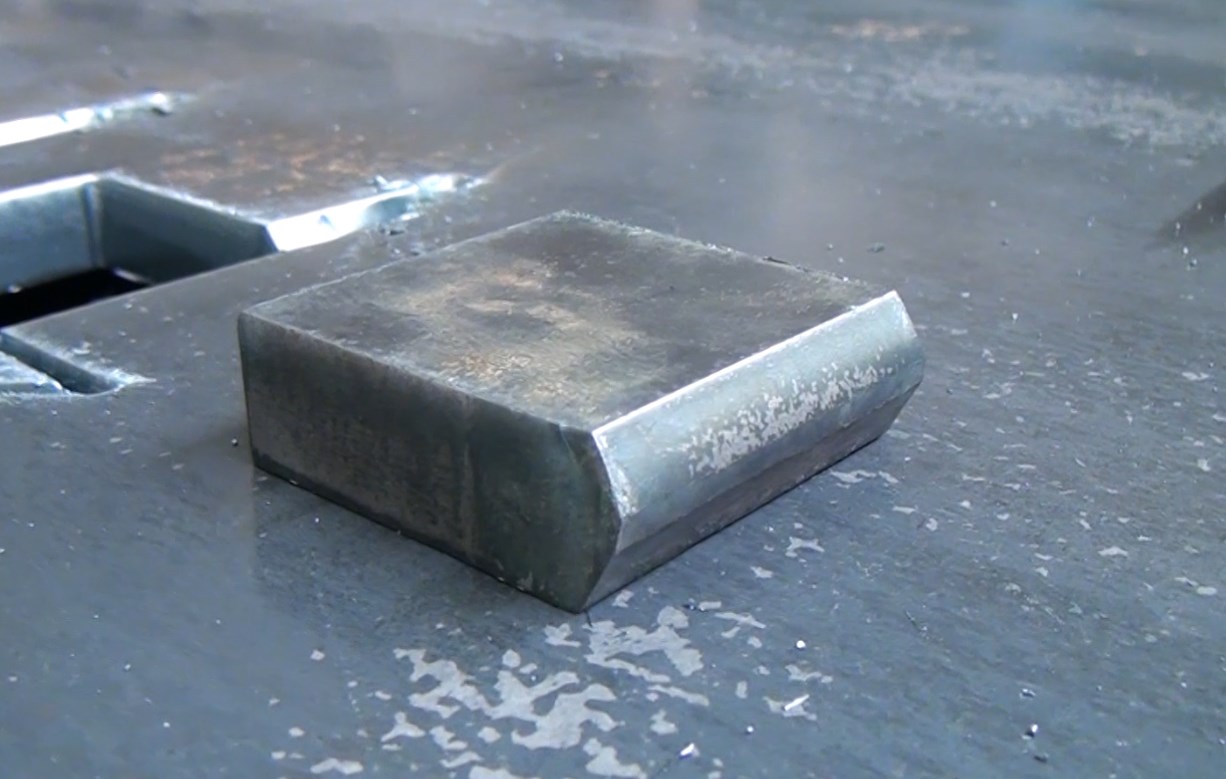
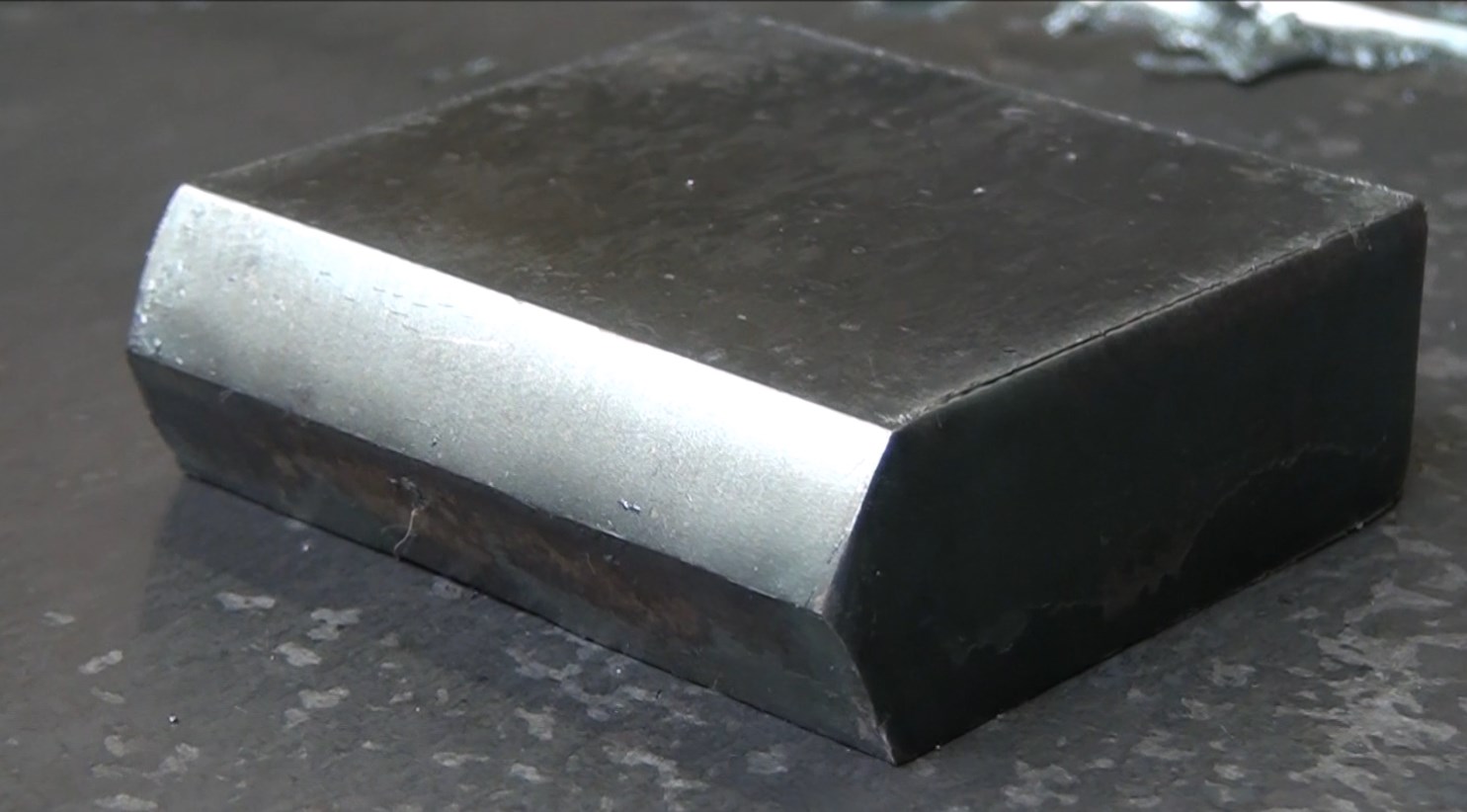
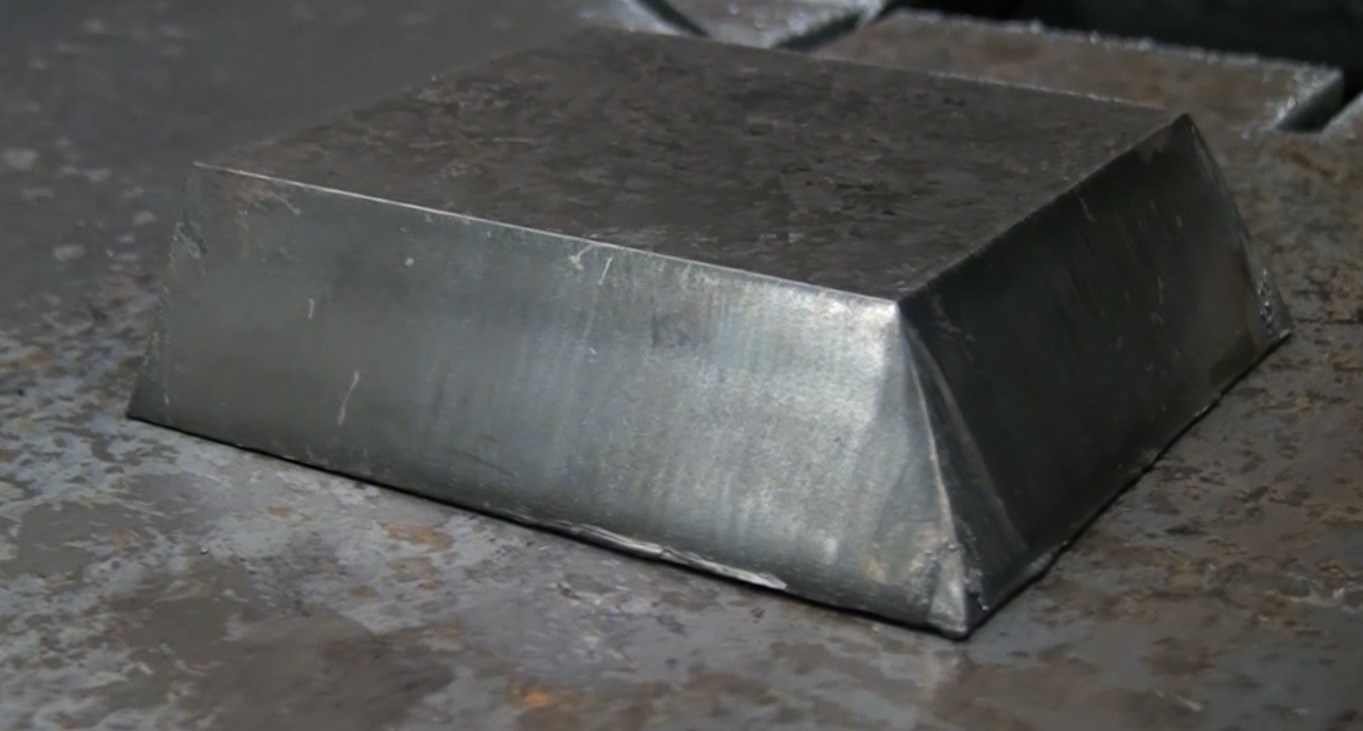
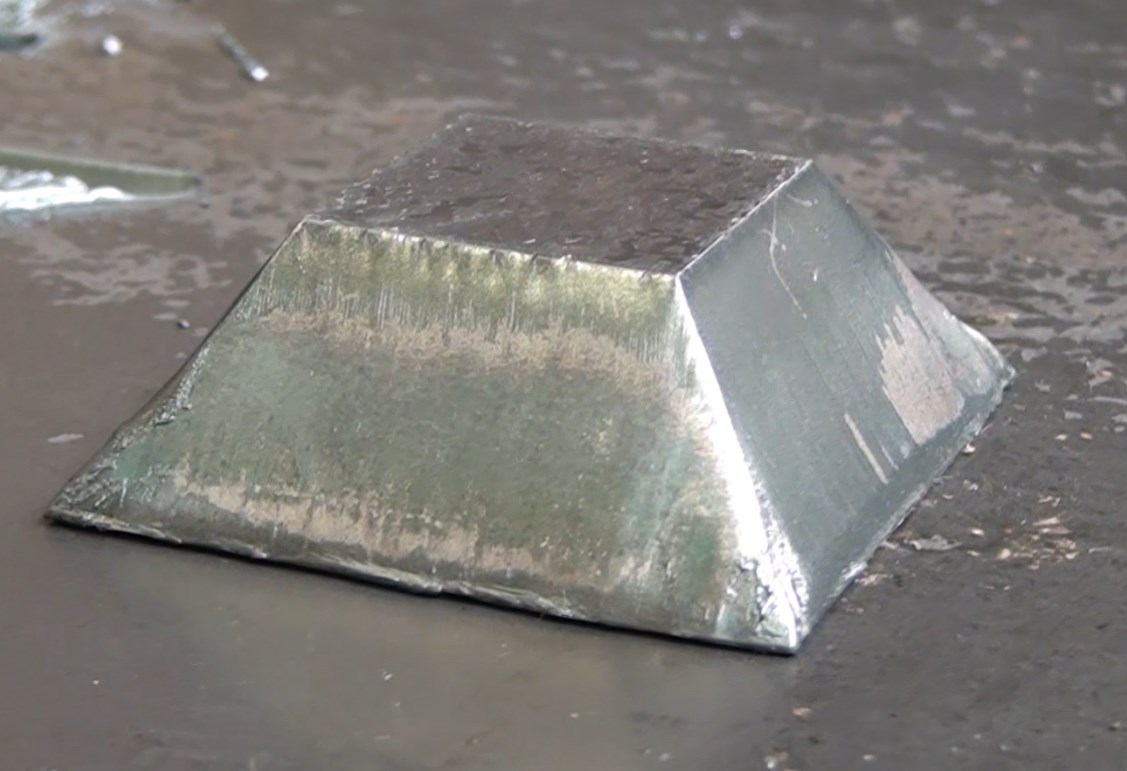
Conventional cutting machines are often only capable of cutting straight. The latest machines often have tilting cutting heads. Thanks to the ability to tilt it is possible to cut a 45° angle. This technique is called bevel cutting.
In some cases it is no longer necessary to use machining operations since the slopes are already created during the plasma cutting proces. In this manner it is possible to make V-cuts, Y-cuts, X-cuts and K-cuts.
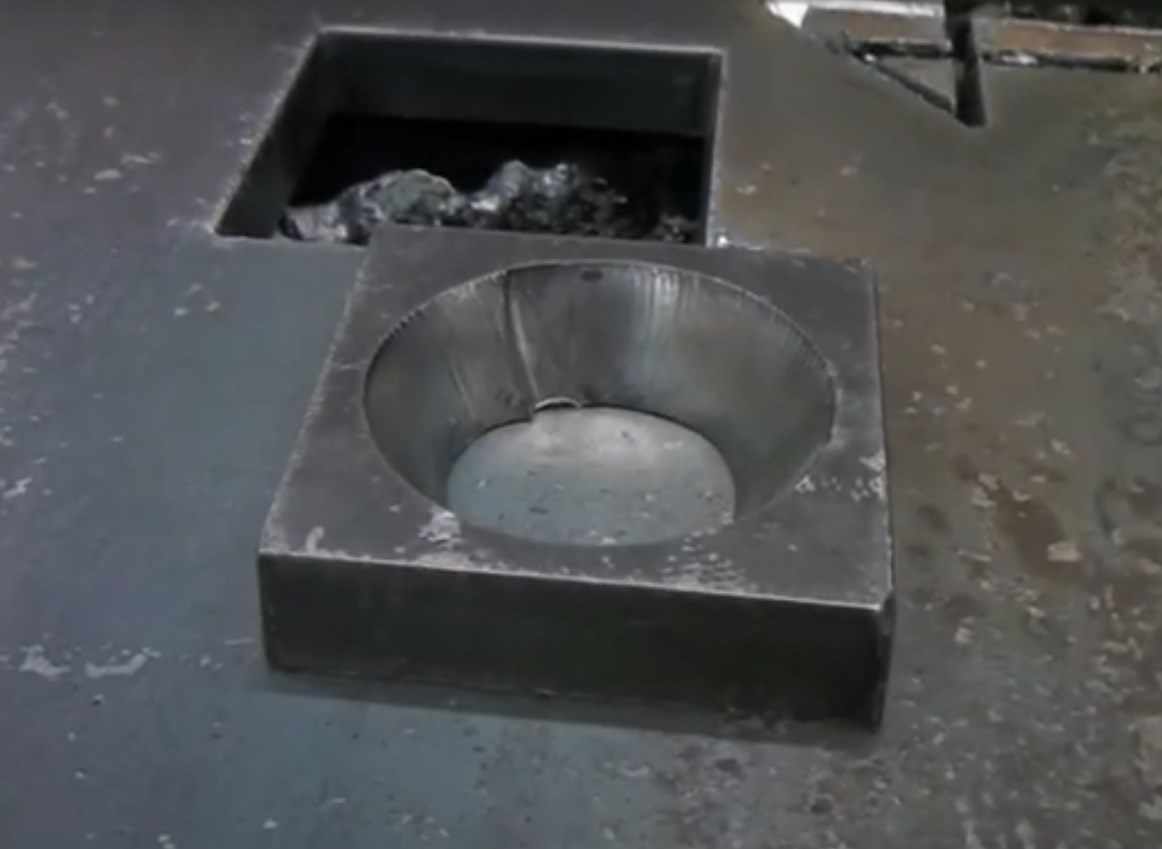







The costs of plasma cutting are influenced by a number of factors:
The cutting speed has a lot of influence on the costs of the production process. This decides the time needed for cutting a series of work pieces. Multiply the cutting time with the hourly costs and this will account for the largest part of the production costs. The cutting speed is influenced by plate thickness and the power of the plasma source.
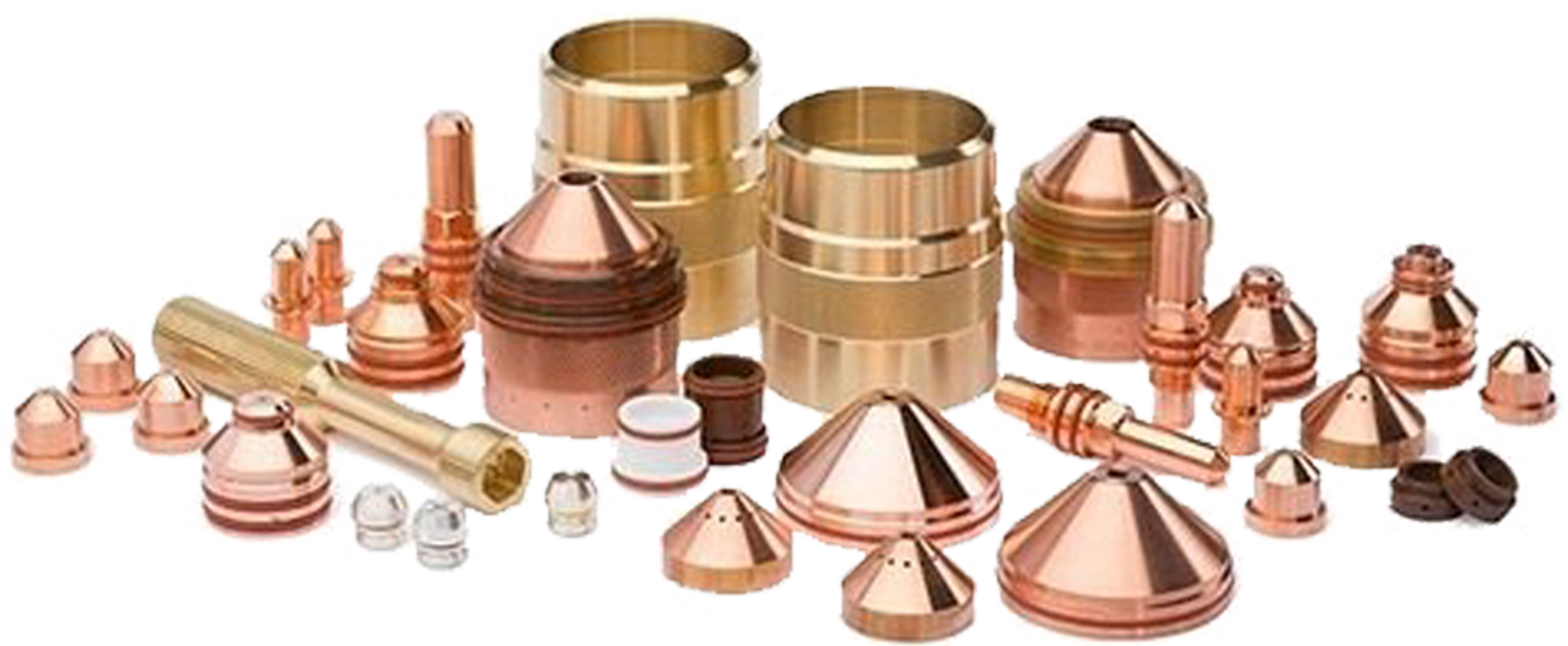
The plasma cutting torch is made out of different wear parts, as for example the nozzle. Molten metal jumps up and ends up on the cover what causes damage. The parts are damaged mainly during the tart of the cutting process or piercing. This makes long contours cheaper than work pieces with many holes.
Using bevel cutting raises the costs, both in the purchase of the machines and the production process that cuts edges multiple times. On the other hand is it no longer necessary to make the welding preparation with a other machining process.
Plates with higher thicknesses take longer to pierce and cut. This lowers the cutting speed and raises the cutting time.
The cutting torch most follow the work piece contour while cutting the plate. Cutting holes takes time as the plate needs to be pierced for every hole. This takes some time and wears the torch a little by each start.
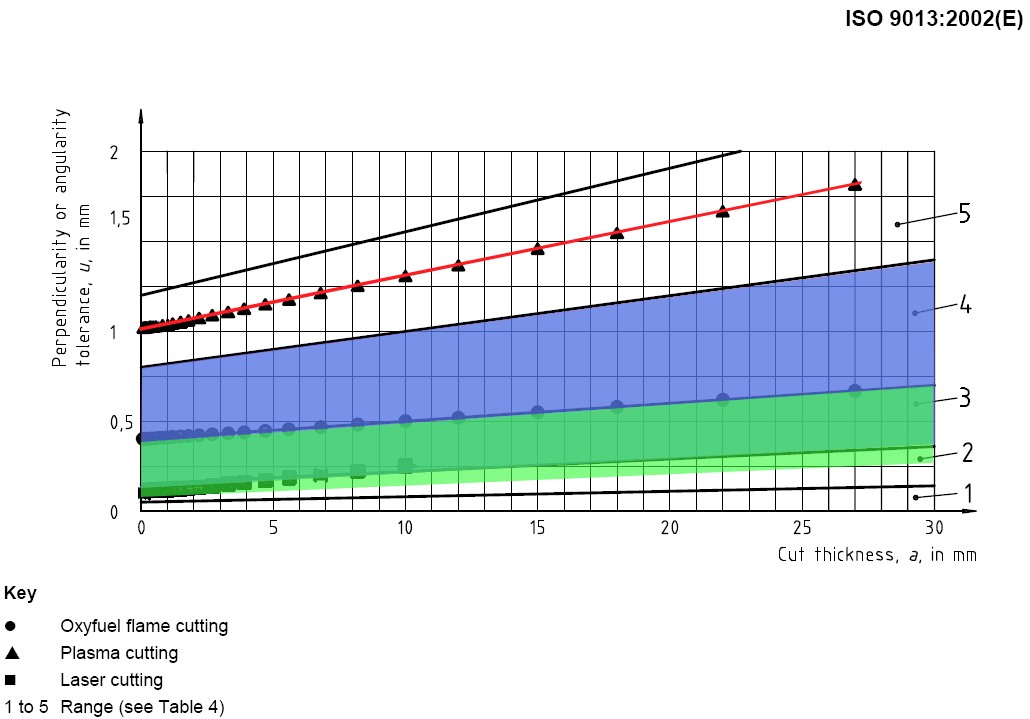
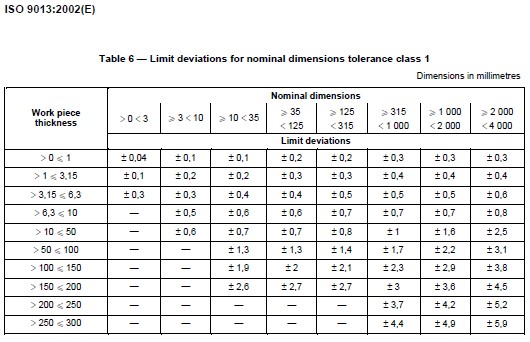
Tolerances also influence the plasma cutting costs. For higher tolerances more time is needed to adjust the radius correction.

Generally, the higher the thickness, the bigger the deviations are.
Contact us for a tailor made offer: https://astratec.eu/contact/
Or reach us here: